Excessive menstrual bleeding can happen for different reasons. Hormonal imbalance and uterine growths are two of the most common causes.
Hormonal Imbalances
Your menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. When they are out of balance, these same hormones can cause heavy periods or bleeding between periods. Causes of hormonal imbalances may include:
- Hormonal changes in teens and women nearing menopause
- Diabetes, thyroid disease or other medical problems
- Obesity
- Stress
- Strenuous exercise
- Anorexia (an eating disorder)
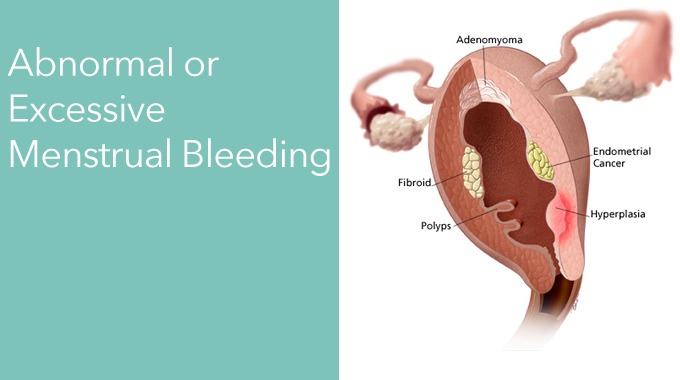
Types of Uterine Growths:
- Fibroids are round “knots” of uterine muscle tissue.
- Adenomyosis occurs when cells of the uterine lining grow into the muscle wall.
- Polyps are small growths of tissue from the uterine lining that grow inside, and often hang into the uterus.
- Hyperplasia is an overgrowth of the uterine lining.
- Endometrial cancer is an uncontrolled growth of cells of the uterine lining in the abdomen.

Treatment Options for Excessive Menstrual Bleeding
Excessive menstrual bleeding can be treated with hormone therapy, surgery or a combination of both options.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy regulates or blocks the hormones that control your menstrual cycle. This means it can limit the swelling of your endometrium and extra endometrial tissue (implants). This treatment may be used before, instead of, or after surgery. The following are different types of hormone therapies:
Surgery
Surgery can be used to remove uterine growths or for a more definitive treatment, to remove the uterus itself. Surgical procedures include endometrial ablation, myomectomy and hysterectomy.